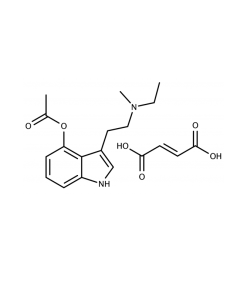
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by indole-fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin, and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin, and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic, and glutamatergic systems.
SUPER
(5)
$37.00 – $62.00
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
SUPER
(5)
$112.00 – $315.00
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
SOLD